Скачать с ютуб BONE STRUCTURE в хорошем качестве
Из-за периодической блокировки нашего сайта РКН сервисами, просим воспользоваться резервным адресом:
Загрузить через ClipSave.ruСкачать бесплатно BONE STRUCTURE в качестве 4к (2к / 1080p)
У нас вы можете посмотреть бесплатно BONE STRUCTURE или скачать в максимальном доступном качестве, которое было загружено на ютуб. Для скачивания выберите вариант из формы ниже:
Загрузить музыку / рингтон BONE STRUCTURE в формате MP3:
Если кнопки скачивания не
загрузились
НАЖМИТЕ ЗДЕСЬ или обновите страницу
Если возникают проблемы со скачиванием, пожалуйста напишите в поддержку по адресу внизу
страницы.
Спасибо за использование сервиса savevideohd.ru
BONE STRUCTURE
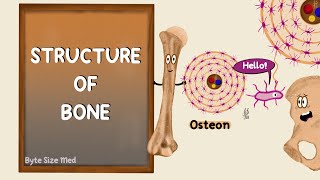
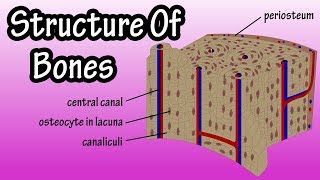
Besides providing structure and support for the body, and allowing for mobility, bones also protect various organs, produce blood cells, and store minerals. These functions are possible thanks to the tissues that make up the bones. There are two types of bone tissue – cortical bone and cancellous bone. Bones also feature other tissue types, including periosteum, endosteum, bone marrow, cartilage, blood vessels, and nerves. Cortical bone, also called compact bone, makes up the hard outer layer of bones. It gives bones their smooth and white appearance and makes up 80% of the total bone mass of the skeleton. An osteon, also called a Haversian system, is the primary anatomical and functional unit of cortical bone. It is a microscopic column that tends to run parallel to a bone’s long axis. Osteons have an osteonic or Haversian canal running through their center, surrounded by concentric rings of matrix called lamellae. Haversian canals allow nerve fibers and blood vessels to pass through and supply the bone. Between the lamellae, you have bone cells called osteocytes in small, oblong spaces called lacunae. I’ll describe osteocytes further later in the video. Canaliculi are tiny passageways that radiate from the Haversian canal to the lacunae. Transverse vessels called Volkmann canals run perpendicular to the osteons and connect adjacent osteons. They also connect blood vessels within osteons to the periosteum. Osteons are densely packed, and spaces between adjacent osteons are filled with interstitial lamellae, which are layers of bone that are generally remnants of previous osteons. Why are there previous osteons? Well, this is due to bone remodeling, or bone metabolism, which is a process in which mature bone tissue is removed through resorption and new bone tissue is added through ossification. Bones are constantly remodelled, because this helps repair microdamages and allows bones to adjust their structure to meet changing mechanical needs. This remodelling is done by specialized cells. Osteoblasts secrete new bone, while osteoclasts break bone down. In addition, there are cells called osteocytes, which result when osteoblasts get trapped in the mineral matrix of bone they’ve created and develop specific features. The space each osteocyte occupies is called a lacuna. Osteocytes can send signals influencing the activity of osteoblasts and osteoclasts and have many other functions. Cortical bone is covered by periosteum on its outer surface, and endosteum on its inner surface. The endosteum forms the boundary between cortical bone and cancellous bone. Cancellous bone, also called trabecular or spongy bone, consists of a porous network. It’s weaker and less dense but more flexible than cortical bone. Cancellous bone accounts for 20% of total bone mass but has nearly 10x the surface area of compact bone. Cancellous bone is highly vascular and often contains red bone marrow where hematopoiesis, the production of blood cells, occurs. It also has a higher surface area to volume ratio compared to cortical bone, which means it’s better for metabolic activities such as the exchange of calcium ions. Anyway, let’s discuss the structure of cancellous bone. Cancellous bone is made up of a network of trabeculae, which are its primary anatomical and functional units. Openings on the trabeculae are called canaliculi and these connect to adjacent cavities, instead of to a haversian canal, for blood supply. Within cancellous bone spaces we find bone marrow and hematopoietic stem cells, which are stem cells that give rise to other blood cells, including platelets, red blood cells and white blood cells. Bone marrow is a nutrient-dense, spongy tissue located in the cavities of bones. It can be found in almost any bone with cancellous tissue and produces both red and white blood cells, as well as platelets. Bone marrow also contains stem cells. In newborns, all such bones are filled exclusively with red marrow or hematopoietic marrow. Red bone marrow produces blood cells. As children age, red bone marrow decreases in quantity and yellow bone marrow increases in quantity. By the age of 25, red bone marrow achieves the final adult distribution. In adults, red marrow is mostly found in the bone marrow of the femur, ribs, and pelvic bones. Yellow bone marrow is located in the hollow cavity of long bones. It is typically found at the center surrounded by red bone marrow. Yellow marrow stores fat and can be called on in life-threatening situations to produce more red blood cells, specifically if you experience rapid blood loss. During these kinds of situations, yellow bone marrow can transform into red bone marrow, producing more blood cells to keep you alive. 3D MODEL: Full Male And Female Anatomy Set Rigged 3D model by 3dMediSphere