Скачать с ютуб Migraine (mechanism of disease) в хорошем качестве
Из-за периодической блокировки нашего сайта РКН сервисами, просим воспользоваться резервным адресом:
Загрузить через ClipSave.ruСкачать бесплатно Migraine (mechanism of disease) в качестве 4к (2к / 1080p)
У нас вы можете посмотреть бесплатно Migraine (mechanism of disease) или скачать в максимальном доступном качестве, которое было загружено на ютуб. Для скачивания выберите вариант из формы ниже:
Загрузить музыку / рингтон Migraine (mechanism of disease) в формате MP3:
Если кнопки скачивания не
загрузились
НАЖМИТЕ ЗДЕСЬ или обновите страницу
Если возникают проблемы со скачиванием, пожалуйста напишите в поддержку по адресу внизу
страницы.
Спасибо за использование сервиса savevideohd.ru
Migraine (mechanism of disease)
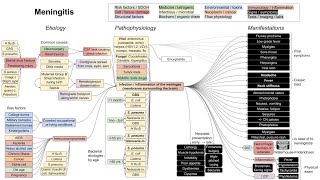
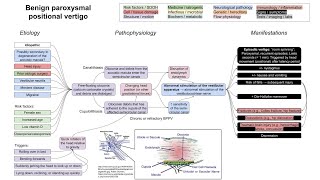
This is a flowchart on migraines, covering the etiology, pathophysiology, and manifestations. ADDITIONAL TAGS: Activation of autonomic nervous system ↑ parasympathetic tone Risk factors / SDOH Cell / tissue damage Nervous system path Migraine Medicine / drugs Infectious / microbial Hormones / metabolic Immunology / inflammation Signs / symptoms Tests / imaging / labs Diet / consumption Genetics / hereditary Flow physiology Pathophysiology Etiology Manifestations Activation of meningeal nociceptors Dilatation of intracranial blood vessels Activation of trigeminal neurons Vasoactive neuropeptides (substance P, CGRP) released Proinflammatory molecules (histamine, bradykinin, serotonin, prostaglandins) released Neurogenic inflammation Trigeminovascular pathway: Wave of depolarization in cerebral cortex Excitation then suppression of neural activity Cortical spreading depression: Vasodilation (might be epiphenomenon): 70%: Genetic predisposition to poor brain habituation to external stimuli (stress, hormonal changes) Hyperexcitable brain Initiation of migraine Dysregulation of pain sensitization in the trigeminal (CN V) system Nausea, vomiting Change in appetite Yawning Fatigue Anxiety Depression Potential triggers Alcohol, nicotine, citrus fruits, dairy, tyramine foods (chocolate, red wine) Poor sleep habits Emotional stress Weather changes Menstruation, hormone intake (OCPs) Lacrimation Nasal congestion Stages of migraine attack: Prodrome (1-2 days before headache): Change in mood Difficulty reading Difficulty writing Aura (25%; lasting 60 min before headache; gradual, reversible): Visual (most common): Scintillating scotoma (arch-shaped visual def, central → peripheral) Flashing lights/spots/lines Blurry vision Distorted color perception Numbness Pins and needles Aphasia Paresis (atypical) Dizziness (atypical) Headache (usually lasting 4-24 hours): Headache; usually unilateral, especially fronto(temporal), retro-orbital; can be pulsating, throbbing, or pounding; worse with physical activity Photophobia Phonophobia Postdrome: Exhaustion Euphoria Muscle weakness Change in appetite