Скачать с ютуб Pharmacology – HEART FAILURE (MADE EASY) в хорошем качестве
Скачать бесплатно Pharmacology – HEART FAILURE (MADE EASY) в качестве 4к (2к / 1080p)
У нас вы можете посмотреть бесплатно Pharmacology – HEART FAILURE (MADE EASY) или скачать в максимальном доступном качестве, которое было загружено на ютуб. Для скачивания выберите вариант из формы ниже:
Загрузить музыку / рингтон Pharmacology – HEART FAILURE (MADE EASY) в формате MP3:
Если кнопки скачивания не
загрузились
НАЖМИТЕ ЗДЕСЬ или обновите страницу
Если возникают проблемы со скачиванием, пожалуйста напишите в поддержку по адресу внизу
страницы.
Спасибо за использование сервиса savevideohd.ru
Pharmacology – HEART FAILURE (MADE EASY)
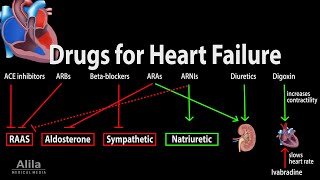
👉 READY TO ACE YOUR EXAM? 📚 GET STUDY NOTES ON PATREON! / speedpharmacology Heart failure is simply defined as a chronic, progressive disorder in which the heart muscle is unable to pump enough blood to meet the body's needs. Depending on the primary cause, heart failure can manifest itself as either systolic or diastolic dysfunction. In systolic heart failure the heart muscle becomes weak and cannot squeeze as much blood out. In diastolic heart failure the heart squeezes normally, but becomes stiff and cannot adequately relax to allow for normal ventricular filling. In the presence of heart failure, in order to counteract the effect of falling cardiac output and thus reduced perfusion to vital organs, the body will try to compensate via two tightly regulated mechanisms. The first one involves the increase in sympathetic nervous system activity. The second one involves the activation of the renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system. This pharmacology lecture discusses mechanism of action of various drugs classes used in management of heart failure including beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs), angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitors, aldosterone antagonists, loop diuretics, vasodilators, and cardiac glycosides. Thanks for watching and don't forget to SUBSCRIBE, hit the LIKE button👍 and click the BELL button🔔 for future notifications!!! 00:00 Heart & Circulatory System 01:40 Types of Heart Failure 02:50 Sympathetic activation 04:05 RAAS activation 06:40 Natriuretic peptides 08:17 Beta-blockers 09:43 ACE inhibitors 10:45 Angiotensin receptor blockers 11:48 ARB/Neprilysin inhibitor 12:56 Aldosterone antagonists 13:43 Loop diuretics 14:45 Vasodilators 16:11 Digoxin