Скачать с ютуб Osmosis Animation and Experiments в хорошем качестве
Скачать бесплатно Osmosis Animation and Experiments в качестве 4к (2к / 1080p)
У нас вы можете посмотреть бесплатно Osmosis Animation and Experiments или скачать в максимальном доступном качестве, которое было загружено на ютуб. Для скачивания выберите вариант из формы ниже:
Загрузить музыку / рингтон Osmosis Animation and Experiments в формате MP3:
Если кнопки скачивания не
загрузились
НАЖМИТЕ ЗДЕСЬ или обновите страницу
Если возникают проблемы со скачиванием, пожалуйста напишите в поддержку по адресу внизу
страницы.
Спасибо за использование сервиса savevideohd.ru
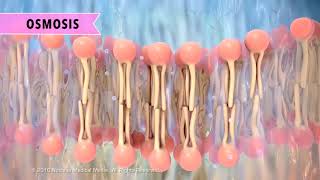
Osmosis Animation and Experiments
Transcript: Before we can talk about osmosis, let’s do a quick review about solutions. Solutions have a solute (like salt, or sugar) that gets dissolved in a solvent (such as water). OK, so now that we know what solutions are, check out this experiment. This tube has a membrane right here that separates two solutions. The solution on the right has a higher concentration of solute and the solution on the left has a lower concentration of solute. Make a hypothesis: what do you think is going to happen? Now, watch what happens over time. Did you notice that the level of blue solution on the right went up and the level of solution on the left went down? Can you explain why this occurs? This happened because of osmosis! Osmosis is the diffusion of water across a semi-permeable or selectively permeable membrane, such as the plasma membrane that surrounds cells. During osmosis, water diffuses down its concentration gradient, from higher to lower water concentration, just like other molecules or ions. You can also say that water moves from an area of lower solute concentration to an area of higher solute concentration. Sometimes this confuses people, but if you think about it, it makes sense. For example, a solution with 1% solute is 99% water, but a solution with 20% solute is only 80% water. The higher the solute concentration, the lower the water concentration, and vice versa. In our experiment, water moved toward the area with the higher solute concentration. Here’s an easy way to remember the direction that water will flow during osmsosis: Water follows solute! If you can remember that, you’re basically all set! But, we do use a few terms to describe relative solute concentrations that you need to know. 1. HYPERTONIC: If we are comparing 2 solutions, the area with the higher solute concentration is HYPERTONIC. Water will always flow across a membrane toward the hypertonic solution! Remember, water follows solute! 2. HYPOTONIC: This is the solution with a lower solute concentration. Water will leave a hypotonic solution by osmosis. 3. ISOTONIC: If two solutions have the same solute concentrations, they are isotonic. The amount of water moving between isotonic solutions is equal so there is no net change in water amounts between the two solutions. Now, let’s look at some real blood cells undergoing osmosis. These cells are in a hypotonic solution. Make a hypothesis: What do you think will happen? The cells popped because water moved into them by osmosis. The cells cytoplasm has a higher concentration of solute than the distilled water that they are floating in, so water rushed in and caused them to explode! Now, let’s look at the opposite effect. Here is an egg that has had its shell removed by being soaked in vinegar overnight. We are going to soak it in corn syrup, a HYPERTONIC solution. Look at how thick the corn syrup is! That is because it is very concentrated with sugar, a solute. Let’s speed this up. Watch what happens as the egg soaks in the Hypertonic corn syrup. Notice how it shrinks and becomes shriveled up, like a raisin. This is because it loses water due to osmosis! To practice more with osmosis, check out the interactive experience at biomanbio.com, linked in the description. If you are enjoying these videos, please feel free to like and subscribe. Blood Cell Video By M. Grundner, U. Klančnik & J. Derganc, Institute of Biophysics, University of Ljubljana, Slovenia: https://www.youtube.com/watch/OYoaLzo... Used with permission: Creative Commons Attribution license (reuse allowed)