Скачать с ютуб Down syndrome, trisomy 21 (mechanism of disease) в хорошем качестве
Из-за периодической блокировки нашего сайта РКН сервисами, просим воспользоваться резервным адресом:
Загрузить через ClipSave.ruСкачать бесплатно Down syndrome, trisomy 21 (mechanism of disease) в качестве 4к (2к / 1080p)
У нас вы можете посмотреть бесплатно Down syndrome, trisomy 21 (mechanism of disease) или скачать в максимальном доступном качестве, которое было загружено на ютуб. Для скачивания выберите вариант из формы ниже:
Загрузить музыку / рингтон Down syndrome, trisomy 21 (mechanism of disease) в формате MP3:
Если кнопки скачивания не
загрузились
НАЖМИТЕ ЗДЕСЬ или обновите страницу
Если возникают проблемы со скачиванием, пожалуйста напишите в поддержку по адресу внизу
страницы.
Спасибо за использование сервиса savevideohd.ru
Down syndrome, trisomy 21 (mechanism of disease)
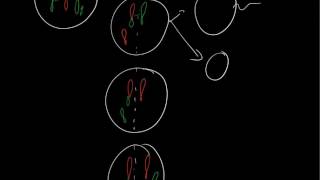
This is a mechanism of disease map for Down syndrome, covering the etiology, pathophysiology, and manifestations. ADDITIONAL TAGS: Behavioral + intellectual disability Risk factors / SDOH Cell / tissue damage Ion channel physio Down syndrome (trisomy 21) Medicine / iatrogenic Infectious / microbial Biochem / molecular bio Other medical conditions Signs / symptoms Tests / imaging / labs Development / intellectual Genetics / hereditary Behavioral / psychiatry Pathophysiology Etiology Manifestations Excess genetic material from chromosome 21 Full trisomy 21 (∼95%): three complete copies of chr 21 Karyotype: ♀: 47,XX,+21 ♂: 47,XY,+21 Spontaneous maternal nondisjunction occurs during meiosis I (70%) or meiosis II (20%) Spontaneous paternal nondisjunction during spermatogenesis, usually meiosis II (5%) High parental age Translocation trisomy 21 (3-4%): third copy of chr 21 is attached to another chr, usually chr 14 → unbalanced Robertsonian translocation By Original from DataBase Center for Life Science (DBCLS)Derivative by Mikael Häggström, M.D. Author info- Reusing images- Conflicts of interest:None Mikael Häggström, M.D. - File:202208 Chromosomal structural abnormality robertsonian translocation icon.svg, CC BY 4.0,https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index... Parent with balanced Robertsonian translocation of long arm of chr 21 to long arm of chr 14 → normal phenotype Karyotype: ♀: 45,XX,t(14;21) ♂: 45,XY,t(14;21) Child with normal karyotype Miscarriage Mosaic trisomy 21 (1-2%): both trisomy 21 cell lines and normal cell lines are present → phenotypes range according to normal:affected ratio Nondisjunction during mitosis that occurs after fertilization Karyotype: ♀: 46,XX/47,XX,+21 ♂: 46,XY/47,XY,+21 Characteristic appearance Organ malformations Endocrine disorders Increased risk of malignancy By Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities - https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/birthdefec..., Public Domain, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index... Eyes: upslanting palpebral fissures, epicanthal folds, Brushfield spots (white/gray in iris); +/- strabismus, cataracts, refractive errors Mouth: small mouth + large tongue = protruding tongue; small teeth with gaps ENT: hypoplastic nasal bones; broad, flat nasal bridge; small round low-set ears w adherent earlobes; short neck, OSA Extrem: transverse palmar crease; sandal gap; clinodactyly (inward curve of 5th finger); short By Loranchet - Own work, CC BY 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index... Heart: atrioventricular septal defect (endocardial cushion defect); +/- ASD, VSD, PDA, ToF GI: duodenal atresia / stenosis; annular pancreas; anal atresia; rectal prolapse; Hirschsprung disease; megacolon; Celiac GU: hypogonadism; cryptorchidism; impaired spermatogenesis → decreased fertility Hypothyroidism Type 1 diabetes ↓ metabolism, ↑ leptin levels, ↓ physical activity → ↑ obesity Delayed motor development, muscle hypotonia Varying intellectual disability (average IQ is 50) Delayed developmental milestones (twice the normal age) Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder; +/- conduct disorder Amyloid precursor protein (on chr 21) → generates amyloid beta -- early onset Alzheimer Autism spectrum disorder Risk of acute lymphoblastic leukemia, acute myeloid leukemia Karyotype: ♀: 46,XX,+21,t(14;21) ♂: 46,XY,+21,t(14;21)