Скачать с ютуб Pulmonary Edema (Fluid In the Lungs) Symptoms & causes в хорошем качестве
Скачать бесплатно Pulmonary Edema (Fluid In the Lungs) Symptoms & causes в качестве 4к (2к / 1080p)
У нас вы можете посмотреть бесплатно Pulmonary Edema (Fluid In the Lungs) Symptoms & causes или скачать в максимальном доступном качестве, которое было загружено на ютуб. Для скачивания выберите вариант из формы ниже:
Загрузить музыку / рингтон Pulmonary Edema (Fluid In the Lungs) Symptoms & causes в формате MP3:
Если кнопки скачивания не
загрузились
НАЖМИТЕ ЗДЕСЬ или обновите страницу
Если возникают проблемы со скачиванием, пожалуйста напишите в поддержку по адресу внизу
страницы.
Спасибо за использование сервиса savevideohd.ru
Pulmonary Edema (Fluid In the Lungs) Symptoms & causes
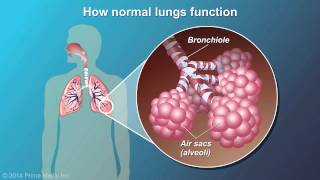
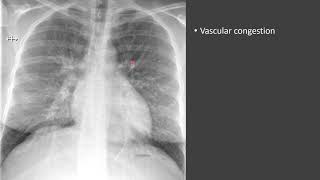
Pulmonary Edema Definition: It refers to the accumulation of fluid in lung tissue, particularly the alveoli. Primary Symptom - Shortness of Breath: This symptom, also known as orthopnea, worsens when lying down and improves when sitting or standing up. Cough with Frothy Sputum: A wet cough producing frothy sputum, sometimes tinged with blood, is a common symptom. Typical Patient Profile: Older individuals with a history of hypertension or heart disease, often overweight or obese. Distinction from Pleural Effusion: Pulmonary edema involves fluid in the lungs, while pleural effusion refers to fluid around the lungs. Diagnostic Tools: X-rays, ultrasounds, and sometimes computed tomography (CT) scans. Heart Failure as a Leading Cause: Accounting for nearly 70% of cases, particularly left-sided heart failure. Fluid Accumulation in Body: Commonly observed in feet and legs due to heart failure. Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS): A severe, emergency condition causing 10-15% of cases. Kidney-Related Causes: Chronic kidney disease or acute kidney injury contributing to 5%-10% of cases. High Altitude Pulmonary Edema (HAPE): Affects young, healthy individuals ascending rapidly to high altitudes. Treatment Methods: Diuretics, vasodilators, inotropic agents, low sodium diet, and exercise. Non-Standard Treatment - Fluid Drainage: Used in cases of pleural effusion, not typically for pulmonary edema itself. Prognosis Dependent on Cause: Acute pulmonary edema is a medical emergency, while chronic is often linked to cardiac issues. Prognosis Variation by Type: Noncardiogenic pulmonary edema generally has a better prognosis than cardiogenic pulmonary edema. Disclaimer: This information is provided for general knowledge and educational purposes only. It is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult with your doctor for any questions or concerns you may have about your health.