Скачать с ютуб Deep vein thrombosis, DVT (mechanism of disease) в хорошем качестве
Скачать бесплатно Deep vein thrombosis, DVT (mechanism of disease) в качестве 4к (2к / 1080p)
У нас вы можете посмотреть бесплатно Deep vein thrombosis, DVT (mechanism of disease) или скачать в максимальном доступном качестве, которое было загружено на ютуб. Для скачивания выберите вариант из формы ниже:
Загрузить музыку / рингтон Deep vein thrombosis, DVT (mechanism of disease) в формате MP3:
Если кнопки скачивания не
загрузились
НАЖМИТЕ ЗДЕСЬ или обновите страницу
Если возникают проблемы со скачиванием, пожалуйста напишите в поддержку по адресу внизу
страницы.
Спасибо за использование сервиса savevideohd.ru
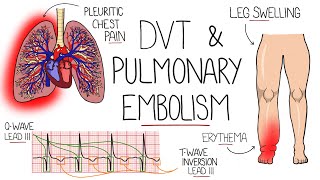
Deep vein thrombosis, DVT (mechanism of disease)
This is a mechanism of disease flowchart for deep vein thromboses (DVT), covering the etiology, pathophysiology, pharmacology, and manifestations. ADDITIONAL TAGS: Lower extremity venous ultrasound: noncompressible obstructed vein, intraluminal hyperechoic mass, distention of affected vein. Doppler: absent/abnormal venous flow, inadequate augmentation of venous flow with distal calf compress or Valsalva Generation of thrombus, typically in lower extremity proximal deep veins → DVT Deep vein thrombosis Medicine / iatrogenic Infectious / microbial Biochem / molecular bio Inflammation / cell damage Signs / symptoms Labs / tests / imaging results Risk factors / SDOH Trauma Blood flow physiology Diet / nutrition Genetics / hereditary Neoplasm / cancer Pathophysiology + pharmacology Etiology Manifestations Virchow's triad Venous stasis Endothelial injury Hypercoag- ulable state Bed rest Immobility Long travel Indwelling cath Recent surgery Infection Chronic disease Prior VTE Smoking Lupus IBD Age 50 Thrombophilias (fVL) Stroke Cancer Nephrotic syndrome Obesity Pregnancy OCPs Exposed collagen and/or endothelium damage Accumulation of procoagulant coagulation cascade proteins Defect or imbalance in coagulation cascade proteins Renal loss of antithrombic factors ↑ estrogen, ↑ progesterone → ↑ prothrombin, ↑ fibrinogen, ↓ protein S Varicose veins Trauma Intrinsic pathway: [Surface contact (collagen, kallikrein, hmwk) → XIIa → XIa → IXa] + [thrombin → VIIIa] Extrinsic pathway: [Damage to endothelial tissue + tissue factor → IIIa] + VIIa Common pathway: [[X → Xa] + [thrombin → Va] → IIa → Ia] + [thrombin + XIIIa] Stable fibrin clot Coagulation cascade Thrombin Heparin, enoxaparin, fondaparinux, dabigatran D dimer Warfarin, phenprocoumon Inhibit vitamin K epoxide redutase: ↓ II, VII, IX, X, C, S Apixaban Rivaroxaban Alteplase (tPA) Plasminogen → plasmin Swelling Tightness Heaviness Dull pain (walk → worse, elevation → better) Calf pain on dorsal flexion of the foot (Homans sign) Fever Patent foramen ovale Stroke symptoms: Numb/weak extremities, confusion, speak / hear / vision deficit, etc Stroke Dyspnea Chest pain Dizziness Weakness DVT travels to lungs → occludes pulmonary arteries / arterioles Pulmonary embolism Unilateral Bacteria Suppurative thrombophlebitis IV drug