Скачать с ютуб Eye Anatomy and Function - Made Easy в хорошем качестве
Скачать бесплатно Eye Anatomy and Function - Made Easy в качестве 4к (2к / 1080p)
У нас вы можете посмотреть бесплатно Eye Anatomy and Function - Made Easy или скачать в максимальном доступном качестве, которое было загружено на ютуб. Для скачивания выберите вариант из формы ниже:
Загрузить музыку / рингтон Eye Anatomy and Function - Made Easy в формате MP3:
Если кнопки скачивания не
загрузились
НАЖМИТЕ ЗДЕСЬ или обновите страницу
Если возникают проблемы со скачиванием, пожалуйста напишите в поддержку по адресу внизу
страницы.
Спасибо за использование сервиса savevideohd.ru
Eye Anatomy and Function - Made Easy
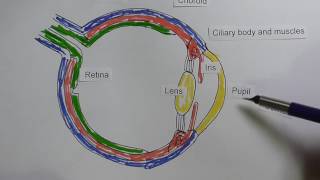
Eye Anatomy and Function - Made Easy (in this video I have explained eye structures/parts of eye/eyeball and it's function Anterior chamber: The region of the eye between the cornea and the lens that contains aqueous humor. Aqueous humor: The fluid produced in the eye. Bruch's membrane: Located in the retina between the choroid and the retinal pigmented epithelium (RPE) layer; provides support to the retina and functions as the 'basement' membrane of the RPE layer. Ciliary body: Part of the eye, above the lens, that produces the aqueous humor. Choroid: Layer of the eye behind the retina, contains blood vessels that nourish the retina. Cones: The photoreceptor nerve cells present in the macula and concentrated in the fovea (the very center of the macula); enable people to see fine detail and color. Cornea: The outer, transparent structure at the front of the eye that covers the iris, pupil and anterior chamber; it is the eye's primary light-focusing structure. Drusen: Deposits of yellowish extra cellular waste products that accumulate within and beneath the retinal pigmented epithelium (RPE) layer. Fovea: The pit or depression at the center of the macula that provides the greatest visual acuity. Iris: The colored ring of tissue behind the cornea that regulates the amount of light entering the eye by adjusting the size of the pupil. Lens: The transparent structure suspended behind the iris that helps to focus light on the retina; it primarly provides a fine-tuning adjustment to the primary focusing structure of the eye, which is the cornea. Macula: The portion of the eye at the center of the retina that processes sharp, clear straight-ahead vision. Optic nerve: The bundle of nerve fibers at the back of the eye that carry visual messages from the retina to the brain. Photoreceptors: The light sensing nerve cells (rods and cones) located in the retina. Pupil: The adjustable opening at the center of the iris through which light enters the eye. Retina: The light sensitive layer of tissue that lines the back of the eye. Retinal Pigmented Epithelium (RPE): A layer of cells that protects and nourishes the retina, removes waste products, prevents new blood vessel growth into the retinal layer and absorbs light not absorbed by the photoreceptor cells; these actions prevent the scattering of the light and enhance clarity of vision. Rods: Photoreceptor nerve cells in the eyes that are sensitive to low light levels and are present in the retina, but outside the macula. Sclera: The tough outer coat that protects the entire eyeball. Trabecular meshwork: Spongy tissue located near the cornea through which aqueous humor flows out of the eye. Vitreous: Clear jelly-like substance that fills the eye from the lens to the back of the eye.