Скачать с ютуб Explain Construction and Working of Double Beam Spectrophotometer. | Spectroscopy | Analytical в хорошем качестве
Скачать бесплатно Explain Construction and Working of Double Beam Spectrophotometer. | Spectroscopy | Analytical в качестве 4к (2к / 1080p)
У нас вы можете посмотреть бесплатно Explain Construction and Working of Double Beam Spectrophotometer. | Spectroscopy | Analytical или скачать в максимальном доступном качестве, которое было загружено на ютуб. Для скачивания выберите вариант из формы ниже:
Загрузить музыку / рингтон Explain Construction and Working of Double Beam Spectrophotometer. | Spectroscopy | Analytical в формате MP3:
Если кнопки скачивания не
загрузились
НАЖМИТЕ ЗДЕСЬ или обновите страницу
Если возникают проблемы со скачиванием, пожалуйста напишите в поддержку по адресу внизу
страницы.
Спасибо за использование сервиса savevideohd.ru
Explain Construction and Working of Double Beam Spectrophotometer. | Spectroscopy | Analytical
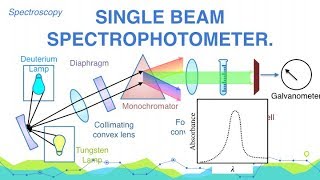
Spectrophotometers are the instruments which are working at a wavelength where the absorbance is maximum. Such wavelength of the radiations whose absorbance is maximum is called λmax. With the help of spectrophotometers we can have qualitative as well as quantitative analysis of any type of sample it may be solid, liquid or gas. It may be colored or colourless. The spectrophotometers are of two types; (i) Single Beam Spectrophotometers, and (ii) Double Beam Spectrophotometers. The following are the main components of a Single Beam Spectrophotometers: 1. Source of radiations: It may be U.V-light, visible light or I.R. light. U.V. Light can be obtained by heating the filament which is filled with either H2 gas or deuterium. Visible Radiations can be obtained by incandescent lamp with tungsten filament and I.R. Radiations can be obtained by heating Newton's glower at the temp. of 1500-2000 oC. Newton's glower is metallic oxide of Yettrium, Erbium and Zirconium. I.R. radiations can also be obtained by heating glow bar which is Silicon carbide SiC (Carborandum) at the temp. of 1300-1700 oC. 2. Collimating Convex Lens: The function is to collect all the rays coming from the source. 3. Diaphragm: To set the 100% transmittance. 4. Monochromators: To obtain the radiation of one wavelength. The Monochromators may be prism or diffraction gratings. 5. Cuvette or Sample Holder: For U.V. light it should be made up of quartz, for visible light it should be made up of glass and for I.R. light it must be that of rock salts for eg. NaCl. a) If the sample is gas or volatile liquid having low B.P. must be taken in the closed container. b) If it is liquid, one drop of the liquid must be placed between two parallel plates for U-V. the plates must be quartz and for visible it must be glass and for I.R. it is rock salt. c) If it is solutions the solvent used for the preparation of solution must be Cyclohexane, methyl alcohol, ethyl alcohol or any other suitable solvent which is not capable to absorb the radiations incident on it. d) If it is solids then we take about 1mg. of it and is mixed in 100-200 mg. of KBr - prepare slurry. It is cut into smaller circular discs (just like bindle) called pellets. They are dried and placed in the place of cuvette. The diameter of pellets is 10mm. and thickness is 1mm. 6. The Focusing Convex Lens: Its function is to collect all the transmitted light from cuvette and is focused at a point where photo cathode of the photo-cell is placed. 7. Photo-Cell: The transmitted light is incident on it photo cathode converts these radiations into current. It can be amplified using the amplifier if needed. 8. Read out meter or dial: The current is converted into OD or Absorbance in read out meter and by knowing OD we can find out the concentration of the solution i.e. quantitative analysis is possible by applying Beer Lamberts Law. First of all the source of radiations from U.V. light to visible light to I.R. radiations is started. The light from the source is collected by Collimating convex lens and allowed to fall on monochromator. For each radiations incident on monochromator we are getting the radiations of one wave length only i.e. λ, the monochromatic light is then separated in two beams with the help of two mirrors M1 and M2. One beam is passed through one cuvette containing blank (solvent) and the other through the other cuvette containing sample solution. Optical attenuator is used to reduce the intensity of radiations coming out from blank to that of the intensity of radiation coming from sample solution and both are finally incident on detectors. These may be photo calls or thermocouples. Where the heat is produced which is then converted to current and finally O.D. or Absorbance (A). The attenuator is connected with pen-which is moving on rotating drum. The graph is obtained on the drum is O D Vs λ. From the graph we can find out λmax and we can have the qualitative analysis. From O.D. or Absorbance we can have the quantitative analysis. Colloidal States - Physical Chemistry • What is Colloidal Solution? | Colloid... Stereochemistry - Organic Chemistry • Explain Configuration and Conformatio... Water and Its Treatment - Engineering Chemistry • Explain why hard water gives out a cu... Electrochemistry - Engineering Chemistry • Distinguish between metallic and elec... Environmental Studies • MCQ on Environmental Studies Part 8 Optics - Applied Physics • What are cartesian sign conventions f... For Details Visit http://cepekmedia.co.nf http://cepek.hol.es/ http://edmerls.66Ghz.com/ http://edmerls.tk/ #DoubleBeam #Spectrophotometer #Spectroscopy #AnalyticalChemistry #Chemistry