Скачать с ютуб VEGF Signalling Pathways в хорошем качестве
Из-за периодической блокировки нашего сайта РКН сервисами, просим воспользоваться резервным адресом:
Загрузить через ClipSave.ruСкачать бесплатно VEGF Signalling Pathways в качестве 4к (2к / 1080p)
У нас вы можете посмотреть бесплатно VEGF Signalling Pathways или скачать в максимальном доступном качестве, которое было загружено на ютуб. Для скачивания выберите вариант из формы ниже:
Загрузить музыку / рингтон VEGF Signalling Pathways в формате MP3:
Если кнопки скачивания не
загрузились
НАЖМИТЕ ЗДЕСЬ или обновите страницу
Если возникают проблемы со скачиванием, пожалуйста напишите в поддержку по адресу внизу
страницы.
Спасибо за использование сервиса savevideohd.ru
VEGF Signalling Pathways
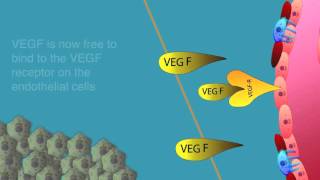
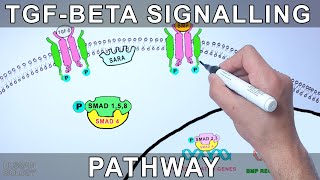
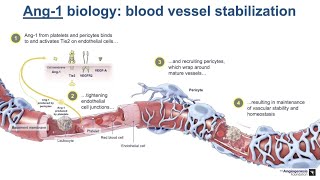
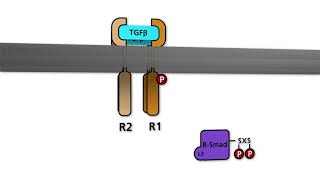
Vascular endothelial growth factor originally known as vascular permeability factor (VPF),[1] is a signal protein produced by many cells that stimulates the formation of blood vessels. To be specific, VEGF is a sub-family of growth factors, the platelet-derived growth factor family of cystine-knot growth factors. They are important signaling proteins involved in both vasculogenesis (the de novo formation of the embryonic circulatory system) and angiogenesis (the growth of blood vessels from pre-existing vasculature). In mammals, the VEGF family comprises five members: VEGF-A, placenta growth factor (PGF), VEGF-B, VEGF-C and VEGF-D. The latter members were discovered after VEGF-A; before their discovery, VEGF-A was known as VEGF. A number of VEGF-related proteins encoded by viruses (VEGF-E) and in the venom of some snakes (VEGF-F) have also been discovered. All members of the VEGF family stimulate cellular responses by binding to tyrosine kinase receptors (the VEGFRs) on the cell surface, causing them to dimerize and become activated through transphosphorylation, although to different sites, times, and extents. The VEGF receptors have an extracellular portion consisting of 7 immunoglobulin-like domains, a single transmembrane spanning region, and an intracellular portion containing a split tyrosine-kinase domain. VEGF-A binds to VEGFR-1 (Flt-1) and VEGFR-2 (KDR/Flk-1).[21] VEGFR-2 appears to mediate almost all of the known cellular responses to VEGF. The function of VEGFR-1 is less well-defined, although it is thought to modulate VEGFR-2 signaling.[22] Another function of VEGFR-1 may be to act as a dummy/decoy receptor, sequestering VEGF from VEGFR-2 binding (this appears to be particularly important during vasculogenesis in the embryo). VEGF-C and VEGF-D, but not VEGF-A, are ligands for a third receptor (VEGFR-3/Flt4), which mediates lymphangiogenesis. The receptor (VEGFR3) is the site of binding of main ligands (VEGFC and VEGFD), which mediates perpetual action and function of ligands on target cells. Vascular endothelial growth factor-C can stimulate lymphangiogenesis (via VEGFR3) and angiogenesis via VEGFR2. Vascular endothelial growth factor-R3 has been detected in lymphatic endothelial cells in CL of many species, cattle, buffalo and primate.[23] In addition to binding to VEGFRs, VEGF binds to receptor complexes consisting of both neuropilins and VEGFRs. This receptor complex has increased VEGF signalling activity in endothelial cells (blood vessels).[12][24] Neuropilins (NRP) are pleiotropic receptors and therefore other molecules may interfere with the signalling of the NRP/VEGFR receptor complexes. For example, Class 3 semaphorins compete with VEGF165 for NRP binding and could therefore regulate VEGF-mediated angiogenesis