Скачать с ютуб Thumb Metacarpal Base Fracture Injury - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim в хорошем качестве
Из-за периодической блокировки нашего сайта РКН сервисами, просим воспользоваться резервным адресом:
Загрузить через ClipSave.ruСкачать бесплатно Thumb Metacarpal Base Fracture Injury - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim в качестве 4к (2к / 1080p)
У нас вы можете посмотреть бесплатно Thumb Metacarpal Base Fracture Injury - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim или скачать в максимальном доступном качестве, которое было загружено на ютуб. Для скачивания выберите вариант из формы ниже:
Загрузить музыку / рингтон Thumb Metacarpal Base Fracture Injury - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim в формате MP3:
Если кнопки скачивания не
загрузились
НАЖМИТЕ ЗДЕСЬ или обновите страницу
Если возникают проблемы со скачиванием, пожалуйста напишите в поддержку по адресу внизу
страницы.
Спасибо за использование сервиса savevideohd.ru
Thumb Metacarpal Base Fracture Injury - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim
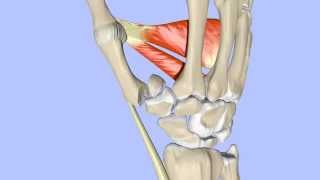
Dr. Ebraheim’s educational animated video describes the fractures of the base of the thumb. There are three types of thumb metacarpal base fractures: 1-Bennett 2-Rolando 3-Extra-articular Anatomy: there are five metacarpal bones in the hand. The first metacarpal bone is connected at the base to the trapezium at the first carpometacarpal joint. The carpometacarpal joint is a saddle shaped joint. The articulation between the first metacarpal bone and the trapezium allows for inherit stability. Both articular surfaces are convex and concave. Movement at the base of the thumb occurs around two axises: flexion/extension, abduction/adduction and rotation. Counting the fingers with the thumb is called opposition. Muscle insertions: abductor pollicis longus (base of metacarpal) and adductor pollicis (base of proximal phalanx). Metacarpal bone fractures 1-Bennett fracture: fracture dislocation that extends into the carpometacarpal (CMC) joint articulation. There is volar-ulnar beak fracture fragment. Mechanism of injury: axial overload along the first metacarpal with simultaneous flexion (“fist fight”). What is the deformity? The key is the volar ulnar beak fracture fragment attached to the palmar oblique ligament. The distal part of the first metacarpal is adducted by the adductor pollicis muscle (ulnar nerve). The metacarpal head is displaced into the palm. The metacarpal shaft is displaced proximally by the abductor pollicis longus muscle (posterior interosseous nerve). The metacarpal is displaced dorsally, radially and supinated. The small volar lip ulnar beak fragment remains in its position attached to the trapezium by the oblique ligament. The main deforming forces are the abductor pollicis longus and the adductor pollicis muscle. The fracture is best seen with hyper pronated AP thumb which is the Robert view and true lateral view. Treatment: closed reduction percutaneous pinning or open reduction internal fixation if the fragment is large enough (more than 20%). Reduce the first metacarpal to restore the articular surface. How to reduce it? Traction longitudinal, pronation of the metacarpal and pressure on the thumb base to push it back to its place by abduction and extension of the metacarpal. Closed reduction and percutaneous pinning are used to treat the majority of cases. The pinning will go from the thumb to the trapezium or from the thumb to the second metacarpal. Pinning may also go to both. Add a thumb spica splint. Accept up to 2 mm of articulation incongruity. The sensory branch of the radial nerve, the radial artery and tendons are in the area. Be aware of these structures during surgery. Be aware of reverse Bennett fractures. Reverse Bennett fracture Fracture of the base of the fifth metacarpal bone which extends into the carpometacarpal (CMC) joint. Intra-articular fracture of the base of the 5th metacarpal. The extensor carpi ulnar is pulling on the 5th metacarpal. 2-Rolando fracture: comminuted intra-articular fracture through the base of the first metacarpal bone with same deformity forces as the Bennett fracture. The base of the 1st metacarpal is split into volar and dorsal fragments. “Y” fracture or transverse fracture. Sometimes three or more intra-articular fragments are present. Treatment is difficult and controversial. Can be ORIF closed reduction percutaneous pinning or external fixation. Prognosis is worse than Bennett and may end in arthritis. The majority of cases do well even with residual displacement or incongruity. 3-Extra-articular fracture has the best outcome. Up to 30 degrees angulation is tolerated well. Thumb CMC is a saddle joint with a lot of mobility. Can treat with thumb splint up to 30 degrees. Angulation more than 30 degrees may lead to MCP hyperextension. Reduce and do closed pinning. In high demand athletes, may use ORIF. Become a friend on facebook: / drebraheim Follow me on twitter: https://twitter.com/#!/DrEbraheim_UTMC Background music provided as a free download from YouTube Audio Library. Song Title: Every Step