Скачать с ютуб Ovarian pathology в хорошем качестве
Из-за периодической блокировки нашего сайта РКН сервисами, просим воспользоваться резервным адресом:
Загрузить через ClipSave.ruСкачать бесплатно Ovarian pathology в качестве 4к (2к / 1080p)
У нас вы можете посмотреть бесплатно Ovarian pathology или скачать в максимальном доступном качестве, которое было загружено на ютуб. Для скачивания выберите вариант из формы ниже:
Загрузить музыку / рингтон Ovarian pathology в формате MP3:
Если кнопки скачивания не
загрузились
НАЖМИТЕ ЗДЕСЬ или обновите страницу
Если возникают проблемы со скачиванием, пожалуйста напишите в поддержку по адресу внизу
страницы.
Спасибо за использование сервиса savevideohd.ru
Ovarian pathology
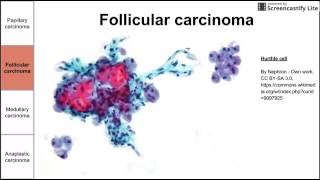
This is a brief video on neoplastic and nonneoplastic diseases of the ovaries. I created this presentation with Google Slides. Image were created or taken from Wikimedia Commons I created this video with the YouTube Video Editor. ADDITIONAL TAGS: Polycystic ovary syndrome Cause: thought to be hyperinsulinemia-related High insulin decreases SHBG, increases LH, increases androgen production Obesity causes decreased SHBG, increased androgens Exclude: CAH, hypothyroidism, hyperprolactinemia, Cushing's Increased risk of endometrial carcinoma (from high estrone) Treatment Hirsutism - flutamide (androgen receptor compet inhibitor), finasteride (5 alpha reductase inhibitor), spironolactone (inhibits steroid binding and syn enzymes), OCPs (lower androgens), metformin (increase insulin sensitivity) Infertility - clomiphene (SERM in brain), letrozole (aromatase inhibitor) Endometriosis Endometrium growing outside of the uterus Endometrial glands and stroma in ectopic locations Most often in the ovaries Occurs via four proposed mechanisms: Retrograde menstruation Dissemination through lymph or blood Iatrogenic (from surgery) Spontaneous (metaplastic differentiation) Histo: need two of the following to diagnose: endometrial stroma endometrial glands hemorrhage and/or hemosiderin-laden macrophages Can progress to endometrioid carcinoma and clear cell adenocarcinoma Cystadenoma Histo: single cells (simple layer), flat lining of non stratified serous or mucinous adenoma Benign bc just single layer of cells Brenner tumor Usually contains urothelium-like cell type (yellow-tan, pale color) Borderline tumor AKA tumor of low malignant potential (LMP) Cystadenocarcinoma Gross: thick, jagged lining; internal papillary excrescences Can also be serous or mucinous Histo: proliferative, malignant lining (invasive), Serous: nuclear hobnailing, psammoma bodies (dystrophic calcification) Mucinous: grey-purple mucin inside cell cytoplasm Clinical: most common in 60s to 70s (postmenopausal women); present late; abdominal/pelvic pain/fullness Serum marker is CA-125 → levels used to guide treatment and recurrence Serous variant is most common malignant ovarian neoplasm Poor prognosis Spreads locally to peritoneum BRCA1 mutation → increased risk for serous variant … BRCA2 and Lynch syndrome also associated Endometrioid variant Usually malignant Can arise from or is associated with endometriosis Granulosa cell tumor Epi: all ages but predominantly women in 50s, late recurrence Low grade malignancy Gross: solid, lobulated Histo: Call-Exner bodies Thecal cell tumor Thecoma Sertoli-Leydig cell tumor Sertoli cells form tubules, derived from male sex cord cells Malignant Leydig cells contain Reinke crystals (rod-like inclusions) Can produce androgens → hirsutism and virilization Can produce estrogen → excess estrogen symptoms Fibroma Benign tumor of fibroblasts Meigs syndrome: pleural effusion and ascites Gorlin syndrome: fibromas of PTCH gene Teratoma When benign: Mature cystic teratoma AKA dermoid cyst Epi: most common germ cell tumor Derived from fetal tissue and 2 or 3 embryologic layers (endoderm, mesoderm, ectoderm) Gross: cystic, 10% bilateral Can contain anything… teeth, hair, bone, thyroid, gut Histo: squamous keratinizing epithelium (if skin), follicles (if hair) Clinical: presents with pain from ovarian enlargement or torsion Benign as long as there are no immature tissues (like neural ectoderm) Immature teratoma Gross: solid Histo: primitive neuroepithelial rosettes (small round layer of blue cells) Struma ovarii Yolk sac tumor AKA endodermal sinus tumor Histo: Schiller-Duval bodies Clinical: increased serum AFP Dysgerminoma Epi: most common malignant germ cell tumor Histo: large cells, central nuclei (with large nucleoli), clear cytoplasm containing glycogen, monotonous cells → “fried egg†cells Clinical: elevated LDH, elevated hCG seminoma Choriocarcinoma Tumor developed from trophoblasts and syncytiotrophoblasts but NO chorionic villi : spreads hematogenously (one of four tumors that do); specifically to lungs Epi: can occur in mother or baby; rare Clinical: hemoptysis, shortness of breath, increased hCG Embryonal carcinoma Krukenberg tumor Consists of mucin filled signet ring cells Gross: glistening surface, because of mucin production Polycystic ovary syndrome Pseudomyxoma peritonei Malignant cancer that spreads from ovaries to intraperitoneal organs Can produce abundant mucin or gelatinous ascites Can fill abdominal cavity, obstruct digestion or organ function Malignancy comes from mucinous adenocarcinoma in ovary Can also come from appendiceal tumor