Скачать с ютуб Parasympathetic Nervous System (Overview, Scheme) | Neuroanatomy в хорошем качестве
Скачать бесплатно Parasympathetic Nervous System (Overview, Scheme) | Neuroanatomy в качестве 4к (2к / 1080p)
У нас вы можете посмотреть бесплатно Parasympathetic Nervous System (Overview, Scheme) | Neuroanatomy или скачать в максимальном доступном качестве, которое было загружено на ютуб. Для скачивания выберите вариант из формы ниже:
Загрузить музыку / рингтон Parasympathetic Nervous System (Overview, Scheme) | Neuroanatomy в формате MP3:
Если кнопки скачивания не
загрузились
НАЖМИТЕ ЗДЕСЬ или обновите страницу
Если возникают проблемы со скачиванием, пожалуйста напишите в поддержку по адресу внизу
страницы.
Спасибо за использование сервиса savevideohd.ru
Parasympathetic Nervous System (Overview, Scheme) | Neuroanatomy
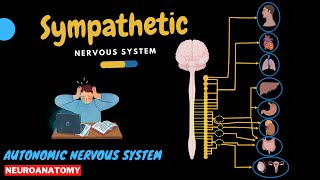
Content: Introduction 0:00 Ganglion and Nucleus 01:35 General Structure 02:06 Sympathetic VS Parasympathetic 02:55 Neurotransmitters 06:10 Craniosacral Outflow 07:35 Cranial Part 08:55 Sacral Part 17:42 Ending 19:19 ------------------------------- 💎Channel membership: / @taimtalksmed 📷 Follow my IG: / taimtalksmed 💝 Donation link: https://www.buymeacoffee.com/taimtalk... ------------------------------- Parasympathetic nervous system is a part of the autonomic nervous system, which is under the motor division of the peripheral nervous system. General Structures and Terms: - Group of cell bodies in CNS - Nucleus - Group of cell bodies outside CNS - Ganglion - Presynaptic neuron is a cholinergic neuron (Ach binds to nicotinic receptors, allowing an influx of cations) - Postganglionic neurons are also cholinergic neurons (Acetylcholine binds to muscarinic receptors of the target organ, activating a g-protein) General Functional Aspects of the Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Divisions: Antagonistic Systems: Territory: - Sympathetic: All areas of the body - Parasympathetic: Not all areas, no innervation in the body wall and limbs Activity: - Sympathetic: More generalized and indirect. Ratio of pre- to postganglionic neurons is 1:15 or more. - E.g., accelerated heart rate, bronchodilation, decreased peristalsis in the gut tube, closing of the sphincters, relaxation of the general bladder wall, and dilation of the pupils. - Parasympathetic: More specific and direct, Ratio of pre- to postganglionic neurons is 1:2 - Decelerated heart rate, bronchoconstriction, increased gut peristalsis, opening of sphincters, contraction of the bladder wall, and constriction of the pupils. Functions: - Sympathetic: Classic ''Fight-or-Flight''. Increase levels of activity and assistance in coping with stress and physical exertion - Parasympathetic: Classic ''Rest-and-Digest''. Homeostasis, restoration, recuperation, and relaxation Complementary (Synergistic) Systems: - Parasympathetic activity produces erection, and sympathetic activity results in ejaculation. Independent function: - Sympathetic activates sweat gland secretion, but parasympathetics play no role in sweat gland activity. Cranial Outflow: - Oculomotor nerve (nervus oculomotorius) - Nucleus: Edinger-Westphal nucleus, accessory oculomotor nucleus (nucleus accessorii nervi oculomotorii) - Synapse with Ciliary ganglion (ganglion ciliare), and innervates the ciliary body and sphincter pupillae - Facial nerve (nervus facialis) - Nucleus: Superior salivatory nucleus (nucleus salivatorius superior) - Greater petrosal nerve synapse with Pterygopalatine ganglion (ganglion pterygopalatinum) to innervate the lacrimal, palatine, nasal and nasopharyngeal glands. - Chorda tympani synapse with Submandibular ganglion (ganglion submandibulare) to innervate submandibular and sublingual glands - Glossopharyngeal nerve (nervus glossopharyngeus) - Nucleus: Inferior salivatory nucleus (nucleus salivatorius inferior) - Lesser petrosal nerve synapse with otic ganglion (ganglion oticum), then innervates the parotid gland - Vagus nerve (nervus vagus) - Nucleus: Posterior nucleus of the vagus nerve (nucleus posterior nervi vagi) - Innervates smooth muscle, glands, internal organs Sacral Outflow: - Sacral parasympathetic nuclei in the lateral horns of the spinal cord as Intermediolateral nucleus (nucleus intermediolateralis) S2, S2, and S4 - Sacral splanchnic nerves (nervi splanchnici sacrales) - Preganglionic fibers going into the inferior hypogastric plexus (plexus hypogastricus inferior) and through organs of the lesser pelvis and synapse with purely parasympathetic ganglia. Sources: - Singh, I. (2017). Human Neuroanatomy (10th ed.). - Wineski, L. E. (2019). Snell’s Clinical Anatomy by Regions (10th ed.). Pearson. - Kozlowski, T. (2017). *Memorix Anatomy: The Complete Study Guide*. 2nd ed. Thieme Medical Publishers. - Fryer, A. D., & Jacoby, D. B. (1998). Muscarinic Receptors and Control of Airway Smooth Muscle. *American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, 158*(Supplement 2), 13tac120. https://doi.org/10.1164/ajrccm.158.su... - Pterygopalatine Ganglion. (n.d.). *ScienceDirect*. Retrieved 20.01.2024. - Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors for Premature Ejaculation: Review of Erectile and Ejaculatory Side Effects - Scientific Figure on ResearchGate. Available from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/F... [accessed 23 Jan, 2024] - University lectures and notes Programs: - Complete Anatomy: https://3d4medical.com/ - Biorender: https://www.biorender.com/ - PowerPoint - Camtasia 2023 Pictures and Visuals used under licenced permission