Скачать с ютуб Endemic fungal infections: Histoplasmosis, (Para)Coccidioidomycosis, Blasto (mechanism of disease) в хорошем качестве
Скачать бесплатно Endemic fungal infections: Histoplasmosis, (Para)Coccidioidomycosis, Blasto (mechanism of disease) в качестве 4к (2к / 1080p)
У нас вы можете посмотреть бесплатно Endemic fungal infections: Histoplasmosis, (Para)Coccidioidomycosis, Blasto (mechanism of disease) или скачать в максимальном доступном качестве, которое было загружено на ютуб. Для скачивания выберите вариант из формы ниже:
Загрузить музыку / рингтон Endemic fungal infections: Histoplasmosis, (Para)Coccidioidomycosis, Blasto (mechanism of disease) в формате MP3:
Если кнопки скачивания не
загрузились
НАЖМИТЕ ЗДЕСЬ или обновите страницу
Если возникают проблемы со скачиванием, пожалуйста напишите в поддержку по адресу внизу
страницы.
Спасибо за использование сервиса savevideohd.ru
Endemic fungal infections: Histoplasmosis, (Para)Coccidioidomycosis, Blasto (mechanism of disease)
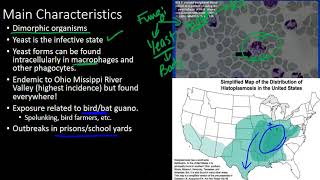
This is a flowchart on the endemic fungal infections, including histoplasmosis, coccidioidomycosis, paracoccidioidomycosis, and blastomycosis, covering the etiology, pathophysiology, and manifestations. ADDITIONAL TAGS: Risk factors / SDOH Cell / tissue damage Structural factors Medicine / iatrogenic Infectious / microbial Biochem / metabolic Immunology / inflammation Signs / symptoms Tests / imaging / labs Environmental / exposure Hereditary / genetic Smooth muscle physiology Pathophysiology Etiology Manifestations Endemic fungal infections Pneumonia and disseminated systemic infection with … Histoplasma capsulatum: Histoplasmosis Coccidioides immitis, Coccidioides posadasii: Coccidioidomycosis (valley fever) Paracoccidioides brasiliensis, Paracoccidioides lutzii: Paracoccidioidomycosis Blastomyces dermatitidis: Blastomycosis Living/travel in endemic areas: Mississippi and the Ohio river valley Exposure to bird / bat droppings in endemic areas via activities like spelunking, cave exploration Immunosuppression (AIDS, medication, hereditary, etc) Living/travel in endemic areas: California, Southwestern USA Soil/dust exposure (e.g., during windstorms, earthquakes, archeological explorations) Living/travel in endemic areas: South and Central America ♂ ♀ (15-fold difference) Living/travel in endemic areas: Southeastern, Central, Eastern, and the Great Lakes region of USA Map from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Asymptomatic Flu-like illness: fever, weight loss, erythema nodosum, hepatosplenomegaly, lymphadenopathy, nonproductive cough Ulcerative oral lesion (palatal, tongue ulcers) CXR: diffuse nodular densities, focal infiltrate or cavity, or LAD Best initial test: positive urine and serum polysaccharide antigen test Silver stain of biopsy or bronchoalveolar lavage showing Macrophages filled with yeast cells that measure 1–5 μm, size RBC Flu-like illness or pneumonia: fever, cough, night sweats, anorexia, chest pain, and dyspnea CNS: meningitis CXR: normal or infiltrates/lymphadenopathy/pleural effusion Sputum, wound exudate, joint effusion → KOH, silver stain, or culture showing: large spherules containing endospores, size RBC Skin: erythema nodosum (desert bumps) Joints: arthralgia (desert rheumatism) Bone: multiple osteolytic lesions Asymptomatic Painful nasal, pharyngeal, and laryngeal mucosal ulcerations Smear (with KOH/calcofluor stain) or tissue biopsy (with silver/PAS stain): budding yeast with “captain's wheel” formation, size RBC Lymphadenopathy (usually cervical) Can disseminate → extrapulmonary manifestations; looks like → Pneumonia: cough, dyspnea, tachycardia, fever Sputum, urine, or body fluids → KOH first, then confirmatory culture: yeast form (at = 37°C), broad-based buds, size = RBC Skin: verrucous lesions and granulomatous nodules (looks like SCC) Bone: osteolytic lesions (in the ribs, vertebrae, and long bones) Genitourinary involvement: prostatitis, orchitis, epididymitis CNS lesions: meningitis, epidural/intracranial abscesses



![Dimorphic Fungi: Paracoccidioidomycosis and Penicilliosis [Hot Topic]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/u-IR6LKsk-U/mqdefault.jpg)