Скачать с ютуб 𝟎𝟓. 𝐈𝐧𝐟𝐫𝐚𝐭𝐞𝐦𝐩𝐨𝐫𝐚𝐥 𝐫𝐞𝐠𝐢𝐨𝐧 (𝐏𝐚𝐫𝐭 𝐈𝐈) (𝐌𝐚𝐱𝐢𝐥𝐥𝐚𝐫𝐲 𝐧𝐞𝐫𝐯𝐞𝐬 + 𝐌𝐚𝐱𝐢𝐥𝐥𝐚𝐫𝐲 𝐚𝐫𝐭𝐞𝐫𝐲 + 𝐏𝐭𝐞𝐫𝐲𝐠𝐨𝐢𝐝 𝐩𝐥𝐞𝐱𝐮𝐬) в хорошем качестве
Из-за периодической блокировки нашего сайта РКН сервисами, просим воспользоваться резервным адресом:
Загрузить через ClipSave.ruСкачать бесплатно 𝟎𝟓. 𝐈𝐧𝐟𝐫𝐚𝐭𝐞𝐦𝐩𝐨𝐫𝐚𝐥 𝐫𝐞𝐠𝐢𝐨𝐧 (𝐏𝐚𝐫𝐭 𝐈𝐈) (𝐌𝐚𝐱𝐢𝐥𝐥𝐚𝐫𝐲 𝐧𝐞𝐫𝐯𝐞𝐬 + 𝐌𝐚𝐱𝐢𝐥𝐥𝐚𝐫𝐲 𝐚𝐫𝐭𝐞𝐫𝐲 + 𝐏𝐭𝐞𝐫𝐲𝐠𝐨𝐢𝐝 𝐩𝐥𝐞𝐱𝐮𝐬) в качестве 4к (2к / 1080p)
У нас вы можете посмотреть бесплатно 𝟎𝟓. 𝐈𝐧𝐟𝐫𝐚𝐭𝐞𝐦𝐩𝐨𝐫𝐚𝐥 𝐫𝐞𝐠𝐢𝐨𝐧 (𝐏𝐚𝐫𝐭 𝐈𝐈) (𝐌𝐚𝐱𝐢𝐥𝐥𝐚𝐫𝐲 𝐧𝐞𝐫𝐯𝐞𝐬 + 𝐌𝐚𝐱𝐢𝐥𝐥𝐚𝐫𝐲 𝐚𝐫𝐭𝐞𝐫𝐲 + 𝐏𝐭𝐞𝐫𝐲𝐠𝐨𝐢𝐝 𝐩𝐥𝐞𝐱𝐮𝐬) или скачать в максимальном доступном качестве, которое было загружено на ютуб. Для скачивания выберите вариант из формы ниже:
Загрузить музыку / рингтон 𝟎𝟓. 𝐈𝐧𝐟𝐫𝐚𝐭𝐞𝐦𝐩𝐨𝐫𝐚𝐥 𝐫𝐞𝐠𝐢𝐨𝐧 (𝐏𝐚𝐫𝐭 𝐈𝐈) (𝐌𝐚𝐱𝐢𝐥𝐥𝐚𝐫𝐲 𝐧𝐞𝐫𝐯𝐞𝐬 + 𝐌𝐚𝐱𝐢𝐥𝐥𝐚𝐫𝐲 𝐚𝐫𝐭𝐞𝐫𝐲 + 𝐏𝐭𝐞𝐫𝐲𝐠𝐨𝐢𝐝 𝐩𝐥𝐞𝐱𝐮𝐬) в формате MP3:
Если кнопки скачивания не
загрузились
НАЖМИТЕ ЗДЕСЬ или обновите страницу
Если возникают проблемы со скачиванием, пожалуйста напишите в поддержку по адресу внизу
страницы.
Спасибо за использование сервиса savevideohd.ru
𝟎𝟓. 𝐈𝐧𝐟𝐫𝐚𝐭𝐞𝐦𝐩𝐨𝐫𝐚𝐥 𝐫𝐞𝐠𝐢𝐨𝐧 (𝐏𝐚𝐫𝐭 𝐈𝐈) (𝐌𝐚𝐱𝐢𝐥𝐥𝐚𝐫𝐲 𝐧𝐞𝐫𝐯𝐞𝐬 + 𝐌𝐚𝐱𝐢𝐥𝐥𝐚𝐫𝐲 𝐚𝐫𝐭𝐞𝐫𝐲 + 𝐏𝐭𝐞𝐫𝐲𝐠𝐨𝐢𝐝 𝐩𝐥𝐞𝐱𝐮𝐬)
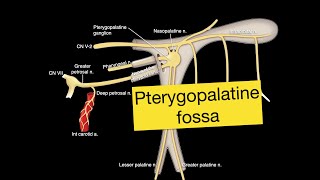
This video describes the maxillary and mandibular nerves' origin, course, and branches. Also, it explains the parts and branches of the maxillary artery, and the formation of the pterygoid plexus of veins (including MCQ, practical, and interactive questions). * 𝐂𝐡𝐚𝐩𝐭𝐞𝐫𝐬 (𝐭𝐢𝐦𝐞𝐬𝐭𝐚𝐦𝐩𝐬) الفصول (الطوابع الزمنية) 00:00 - Intro (مقدمة) 00:23 - Content (المحتوى) 00:43 - Maxillary nerve 01:04 - Origin 02:22 - Course 10:04 - Branches 13:00 - Maxillary artery 13:10 - Origin 14:10 - Course 15:26 - Branches 15:50 - Branches of the first part 17:15 - Branches of the second part 18:09 - Branches of the third part 19:08 - Branches of the infratemporal artery 20:48 - Pterygoid plexus of veins 20:57 - Site 21:31 - Tributaries 22:22 - Drainage 22:51 - Function 24:26 - Connections 26:14 - MCQ 27:19 - Practical questions 28:16 - Interactive questions * 𝐏𝐨𝐬𝐭𝐞𝐫𝐢𝐨𝐫 𝐬𝐮𝐩𝐞𝐫𝐢𝐨𝐫 𝐚𝐥𝐯𝐞𝐨𝐥𝐚𝐫 (𝐏𝐒𝐀) 𝐧𝐞𝐫𝐯𝐞 𝐛𝐥𝐨𝐜𝐤: - It anesthetizes maxillary molar teeth. With the PSA nerve block, the first molar may not be completely anesthetized; in this case, the PSA nerve block can be used in conjunction with an MSA/supraperiosteal block. Approach: The needle is inserted at the height of the muco-buccal fold above the maxillary second molar at a 45-degree angle aimed superiorly, medially, and posteriorly. * 𝐌𝐢𝐝𝐝𝐥𝐞 𝐬𝐮𝐩𝐞𝐫𝐢𝐨𝐫 𝐚𝐥𝐯𝐞𝐨𝐥𝐚𝐫 (𝐌𝐒𝐀) 𝐧𝐞𝐫𝐯𝐞 𝐛𝐥𝐨𝐜𝐤: - It anesthetizes the maxillary premolars with occasional overlap to the canine and first molar Approach: Penetration for the MSA injection is at the height of the buccal vestibule lateral to the maxillary second premolar. The needle tip should approximate the apex of the tooth, which usually requires a penetration of about 5 mm. * 𝐀𝐧𝐭𝐞𝐫𝐢𝐨𝐫 𝐬𝐮𝐩𝐞𝐫𝐢𝐨𝐫 𝐚𝐥𝐯𝐞𝐨𝐥𝐚𝐫 (𝐈𝐧𝐟𝐫𝐚𝐨𝐫𝐛𝐢𝐭𝐚𝐥) 𝐧𝐞𝐫𝐯𝐞 𝐛𝐥𝐨𝐜𝐤: - It anesthetizes the maxillary central and lateral incisors and canine as well as the surrounding soft tissue on the buccal aspect. Approach: Insert the needle into the muco-buccal fold with the bevel-facing bone, aligned with the center of the tooth to be anesthetized, aimed toward the maxilla. Contact the maxilla, then withdraw the needle 1 mm. Aspirate. Slowly inject 1-2 mL of local anesthetic at the apex of the root tip. * 𝐖𝐡𝐚𝐭 𝐢𝐬 𝐭𝐡𝐞 𝐦𝐨𝐬𝐭 𝐝𝐢𝐟𝐟𝐢𝐜𝐮𝐥𝐭 𝐭𝐨𝐨𝐭𝐡 𝐭𝐨 𝐚𝐧𝐞𝐬𝐭𝐡𝐞𝐭𝐢𝐳𝐞? It has been generally accepted that mandibular molars are the most difficult teeth to anesthetize, especially if irreversible pulpitis is present. * 𝐆𝐞𝐧𝐞𝐫𝐚𝐥 𝐫𝐮𝐥𝐞 𝐟𝐨𝐫 𝐥𝐨𝐜𝐚𝐥 𝐚𝐧𝐞𝐬𝐭𝐡𝐞𝐬𝐢𝐚: - Local anesthesia can usually be placed right next to the teeth to be worked on. * 𝐇𝐨𝐰 𝐭𝐨 𝐬𝐭𝐨𝐩 𝐛𝐥𝐞𝐞𝐝𝐢𝐧𝐠 𝐟𝐫𝐨𝐦 𝐭𝐡𝐞 𝐦𝐚𝐱𝐢𝐥𝐥𝐚𝐫𝐲 𝐚𝐫𝐭𝐞𝐫𝐲? Firm pressure with the forefinger applied intra-orally and directed posterolaterally in the region of the maxillary tuberosity immediately controls bleeding from the vessels medial to the TMJ. * 𝐖𝐡𝐚𝐭 𝐢𝐬 𝐭𝐡𝐞 𝐩𝐭𝐞𝐫𝐲𝐠𝐨𝐢𝐝 𝐩𝐮𝐦𝐩? - The pterygoid plexus functions to return the blood to the heart; this occurs during the movement of the lateral pterygoid, generating a pumping action of the blood back to the heart. * 𝐖𝐡𝐢𝐜𝐡 𝐟𝐫𝐚𝐜𝐭𝐮𝐫𝐞 𝐢𝐬 𝐚𝐬𝐬𝐨𝐜𝐢𝐚𝐭𝐞𝐝 𝐰𝐢𝐭𝐡 𝐭𝐡𝐞 𝐦𝐚𝐱𝐢𝐥𝐥𝐚𝐫𝐲 𝐚𝐫𝐭𝐞𝐫𝐲? - The maxillary artery lies in close relation to the medial cortex of the distal part of the condylar process and is vulnerable to injury by the sharp edges of the fracture fragments during the initial trauma or during operative fracture reduction. - Maxillary artery injuries and subcondylar fractures may be an underdiagnosed phenomenon. * 𝐌𝐂𝐐: 1. A 27-year-old patient complained of acute dental pain due to caries of the 3rd maxillary molar teeth. Which of the following nerves supply this tooth? A. Lingual B. Buccal C. Mental D. Posterior superior alveolar 2. During surgical removal of a tumor in the infratemporal fossa, there was an intense hemorrhage. The surgeon clamped the main source of arterial supply to the area, which is the: A. Lingual B. Maxillary C. Superficial temporal D. Posterior auricular 3. Which of the following arteries is a branch of the third part of the maxillary artery? A. Middle meningeal B. Inferior alveolar C. Deep temporal D. Greater palatine 😂💞 🤣 𝓦𝓪𝓲𝓽𝓲𝓷𝓰 𝓕𝓸𝓻 𝓨𝓸𝓾𝓻 𝓐𝓷𝓼𝔀𝓮𝓻 😂💞 🤣 * 𝐅𝐨𝐫 𝐜𝐨𝐧𝐭𝐚𝐜𝐭: 📌𝐄𝐦𝐚𝐢𝐥: [email protected] 📌𝐅𝐚𝐜𝐞𝐛𝐨𝐨𝐤 𝐩𝐞𝐫𝐬𝐨𝐧𝐚𝐥 𝐚𝐜𝐜𝐨𝐮𝐧𝐭: / drayman.khanfour 📌𝐅𝐚𝐜𝐞𝐛𝐨𝐨𝐤 𝐠𝐫𝐨𝐮𝐩: / 314015989895733 📌𝐓𝐞𝐥𝐞𝐠𝐫𝐚𝐦 𝐜𝐡𝐚𝐧𝐧𝐞𝐥: https://t.me/+k-LcyYc-0WsyNDg0 📌𝐓𝐞𝐥𝐞𝐠𝐫𝐚𝐦 𝐠𝐫𝐨𝐮𝐩: https://t.me/+S-dZx8Sf-LBiOWE0 📌𝐈𝐧𝐬𝐭𝐚𝐠𝐫𝐚𝐦: / dr_aymn 📌𝐘𝐨𝐮𝐓𝐮𝐛𝐞 𝐜𝐡𝐚𝐧𝐧𝐞𝐥 𝐰𝐞𝐛𝐬𝐢𝐭𝐞 𝐥𝐢𝐧𝐤: / @dr.ayman_khanfour 📌𝐌𝐨𝐛𝐢𝐥𝐞 (𝐚𝐧𝐝 𝐖𝐡𝐚𝐭𝐬𝐀𝐩𝐩): +20 1223815866 * 𝐇𝐚𝐬𝐡𝐭𝐚𝐠: #maxillary_nerve #maxillary_artery #pterygoid_plexus





![Divine Music - Ethnic & Deep House Mix 2024 [Vol.49]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/kMrRQB4XD-U/mqdefault.jpg)


